According to the International Journal Of Health Sciences, diabetes is a major public health problem that is approaching epidemic proportions globally. Worldwide, the prevalence of diabetes is increasing at an alarming rate.
Contents
This rapid increase can be linked to lifestyle and diet changes that mimic those of the Western world. The more junk food available and time spent on the couch or in a chair, the greater the incidence of diabetes.
Complications from diabetes, such as coronary artery and peripheral vascular disease, stroke, diabetic neuropathy, amputations, renal failure and blindness result in increasing disability, reduced life expectancy and enormous health costs for virtually every society. Diabetes is certain to be one of the most challenging health problems in the 21st century. [1]

What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes refers to a group of diseases that adversely affect how your body uses blood glucose (blood sugar). The end result is your body’s inability to move glucose into your cells and in extreme cases, your cells starve.
According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) Diabetes Atlas, approximately 400 million people around the world suffer from diabetes. Nearly half of those are adults aged 40-59 years. The number of people with type 2 diabetes is increasing in every single country worldwide and the IDF estimates there will be more than 600 million diabetics by 2035.
If untreated, diabetes can cause serious health complications including heart disease, blindness, kidney failure, and eventual extremity amputations. Diabetes remains the 6th leading cause of death in the US. The use of alcohol and tobacco products multiplies the health risks associated with diabetes.
Types Of Diabetes
1. Type I Diabetes (Insulin Dependent Diabetes) - Type I diabetes is most prevalent in children and young adults and is the result of the pancreas failing to produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that breaks down sugars and starches while converting them into energy and acts as a “key” that opens cell walls for transporting glucose into the cell.
2. Type II Diabetes (Non Insulin Dependent Diabetes) - Type II diabetes occurs later in an adult's life and is caused by either the pancreas being unable to produce enough insulin or the cells in your body ignore the insulin and are unable to utilize glucose. When your cells ignore the insulin, the condition is referred to as insulin resistance.
3. Gestational Diabetes - Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually disappears after delivery. An estimated 3% of all pregnancies are complicated by gestational diabetes and nearly half of those mothers are at risk of developing permanent diabetes later.
Treating Diabetes

Traditional treatments to help control Type I Diabetes include a healthy low carb diet, moderate physical activity and insulin injections. The amount of insulin required is determined by your food intake and daily activity. For patients with Type I Diabetes, blood glucose levels must be closely monitored (using blood glucose meters) through frequent “finger sticks” or blood glucose testing.
Treatment for Type II Diabetes includes a low carb healthy diet, increased physical activity, body weight maintenance and may include blood glucose testing. Many people with Type II Diabetes benefit from oral medication and/or insulin to control their blood glucose levels. Oral medications work by stimulating your pancreas to make more insulin to balance glucose in the bloodstream.
Changes in lifestyle are your best option for countering any type of diabetes. Increased regular exercise, maintaining a healthy body weight combined with a reduction of sugar and fat intake. A high fiber diet will also help. The combination of these healthy changes will increase insulin sensitivity as well as maintain a healthy blood pressure.
Rates Of Diabetes By Country Or Region
Statistics for diabetes can be compiled and presented in two ways, as a percentage of the country’s total population, or as the total number of the population affected. For example:
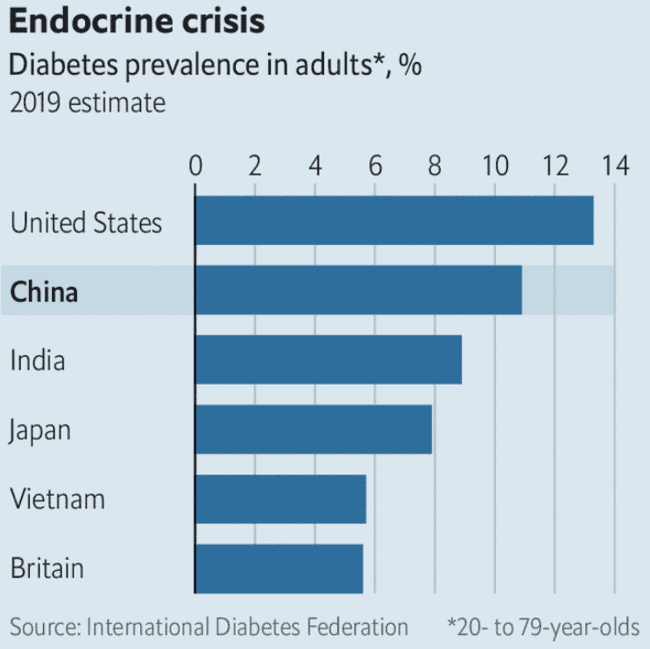
- CHINA has the highest TOTAL NUMBER of diabetics worldwide with around 116 million people suffering from the disease. But, as a PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL POPULATION, at 9.2% China ranks 60th of 195 countries tracking diabetes data. It is interesting to note that in 2010, only 4.2% of the Chinese population were affected by diabetes. The percentage has more than doubled in that nine year period and can be attributed to dietary and lifestyle changes. More fast foods (burgers, sodas and fried chicken) and less natural fish and vegetables!
- INDIA ranks number two in TOTAL NUMBER of diabetics at 77 million. India ranks 46th of 195 countries as a PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL POPULATION, at 10.4%.
- The UNITED STATES ranks third with a TOTAL NUMBER of diabetics at 31 million, but ranks 43rd of 195 countries as a PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL POPULATION, at 10.8%.
- PAKISTAN ranks fourth with a TOTAL NUMBER of diabetics at 19 million, but ranks 6th of 195 countries as a PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL POPULATION, at 19.9%.
- BRAZIL ranks fifth with a TOTAL NUMBER of diabetics at 17 million, but ties with India at 46th of 195 countries as a PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL POPULATION, at 10.4%.
- MEXICO ranks sixth with a TOTAL NUMBER of diabetics at 13 million, but ranks 20th of 195 countries as a PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL POPULATION, at 13.5%.
- INDONESIA ranks seventh with a TOTAL NUMBER of diabetics at 11 million, but ranks 108th of 195 countries as a PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL POPULATION, at 6.3%.
- GERMANY ranks eighth with a TOTAL NUMBER of diabetics at 9.5 million, but ties with India and Brazil at 46th of 195 countries as a PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL POPULATION, at 10.4%.
PREDICTIONS 2045 - By the year 2045, it is predicted that India will have around 134 million people with diabetes. While the country with the highest projected number of diabetics in 2045 is China, with a projected 147 million people between the ages of 20 and 79 suffering from diabetes. It is also forecast that the number of adults with the condition in Pakistan will exceed that of the United States by 2045.
The Pacific Islands And Diabetes
While it is clear that countries with very large populations have large numbers of diabetics, a number of very small Pacific islands with very small populations have the largest percentages of diabetics. The highest percentages include: Kiribati, Tuvalu, Mauritius, New Caledonia, Solomon Islands and Papua New Guinea all at about 20% of their total population. This means that one of every five of these Pacific Islanders is diabetic. In the Marshall Islands, the percentage is above 30%, one of every three inhabitants is diabetic!
Why such a high incidence of diabetes in these similar small islands? Pacific Islanders are more than three times more likely to be diagnosed with diabetes, compared to non-Hispanic whites. This is due to higher rates of risk factors such as being overweight and obese, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking. This population of Pacific Islanders has a genetic predisposition to obesity and when exposed to Western lifestyles following World War II this predisposition resulted in high rates of obesity and diabetes.
Who is most susceptible to developing diabetes? Aside from the Pacific Islanders mentioned above at 20-30%, prevalence of diagnosed diabetes is highest among Native American Indians and Alaskan Natives (14.7%), people of Hispanic origin (12.5%), and non-Hispanic blacks (11.7%), followed by non-Hispanic Asians (9.2%) and non-Hispanic whites (7.5%). Worldwide, Asian Indians have the highest diabetes prevalence rate (14.2%), whereas Asian people from Korea and Japan have the lowest diabetes prevalence rates at 4.0% and 4.9%, respectively.
What gender is diabetes most common in? Diabetes is more common in males than in females. However, females who do develop diabetes often have more serious complications (heart disease, vascular disease and kidney disease) and a greater risk of death from these complications.
At what age are you most likely to develop diabetes? Middle-aged and older adults are at the highest risk for developing diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes.
According to the CDC's National Diabetes Statistics Report, there were an additional 1.5 million newly diagnosed diabetes cases among adults during 2015. In that year, adults aged 45 to 64 were the most diagnosed age group for diabetes.
Is diabetes hereditary? Both types of diabetes, type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes can be inherited. This means a group of genes that can lead to diabetes can be passed down from mothers and fathers to their children.
Not everyone who inherits the genes will develop it, but if you have the genes for diabetes, you've got a greater chance of developing it. In the case of type 2 diabetes, if you are also obese, eat a poor (high sugar) diet high in processed foods and carbohydrates leading to insulin resistance, you will be at much greater risk.
What Countries Have The Lowest Rates Of Diabetes?
Not surprisingly, the countries with the lowest incidence of diabetes are African countries with the least Western influence. The list includes Nigeria, Kenya, Ghana, Uganda, Togo, Mali, Liberia, Senegal and Zimbabwe. These countries remain at or below 2% of their total population with diabetes diagnosis.
Aside from Africa, the countries with the lowest incidence of diabetes include Lithuania, Estonia, and Ireland (at an average of 4% of the total population), followed by Sweden, Luxembourg, Britain and Australia (with an average of around 5% of the total population).
Conclusions
The prevalence of diabetes is directly linked to a country's economic development combined with the spread of sedentary Western lifestyles and diet to developing countries, resulting in substantial increases in diabetes.
Without effective education, prevention and control programs, diabetes will likely continue to increase well into the future.