By the year 2050, the world’s aging population is projected to double. People everywhere are living longer, which brings new concerns for prevention of the chronic conditions that come with aging.
That’s 12 percent more people over the age of 60 who will be living on our planet by then, a full 22 percent of the population. In numbers, it is 900 million now, and 2 billion by 2050 who will be in the senior population.
We are constantly searching for that fountain of youth, that magic pill, or the lifestyles that will keep us fit and well in the future as we grow older. It’s not just getting to the golden years that is the goal; it’s getting there without chronic health issues to keep you from enjoying your retirement.
Quality of life becomes more important than quantity of life, as we search for ways to age not only gracefully, but have a working body and mind that carries us through our old age.
So, what are some of the things that you can do to prevent or delay common health issues related to aging?
It’s true that some conditions are just a part of aging, such as loss of muscle tone in facial features, causing sagging skin and wrinkles. These can be prevented to some extent, or remedied with major plastic surgeries, but most of us learn to accept that aging is a natural process and find a way to accomplish it with grace and dignity.
Normal changes that occur with aging vs the changes we can prevent
While there are some aspects of the aging process that we can’t change, we may be able to lessen the symptoms associated to them, or get treatments for them. Others are not easily ignored if we decide to turn a blind eye on them. Something like diabetes can lead to debilitating complications in every bodily organ if left unchecked and unmanaged.
In this article, we will look at the common chronic conditions and problems that we can develop as we age. We will also look at the prevalence of these conditions in the aging population and ways to prevent them. We will see what the common available treatments are if you develop them.
The prevalence of chronic health conditions in an aging population
Between 50% to 70% of senior adults have at least one chronic health condition, and over 75 percent of them have two or more chronic health conditions.
Chronic diseases are not only debilitating physically, but they are also costly to the person with the chronic condition and to the society. The following are the most often found chronic health conditions in the elderly, and they account for most of the healthcare costs in the aging population; cardiovascular disease, stroke, cancers and diabetes.
Role of diet, exercise and lifestyle changes
Staying physically fit and eating a healthy diet are important to preventing the onset of chronic conditions as we age. It’s also important to get all your preventative check-ups and see your health care provider regularly.
The Centers for Disease Control’s (CDC) offers health information for those in the aging population. You can link to their full aging guide here: https://www.cdc.gov/aging/aginginfo/index.htm
If you’re not yet a senior, start a wellness program now
If you’re looking to prevent as many of the effects of aging that you possibly can, and you’re still young, it’s a great idea to get your wellness program jump started right now. Don’t wait till later to set your goals. Go through the list of the chronic conditions and find out ways in which they can be prevented.
Physical changes are a natural part of aging, and occur in every organ.
There are some diseases and chronic conditions that are more prevalent in the elderly.
If you take steps to make lifestyle changes now, you can prevent common health problems related to aging.
It is important to have regular checkups and routine prevention screenings.
I recommend reading the following article:
Contents
- List of the most common health concerns for the elderly and senior
- Heart disease and stroke
- Arthritis
- Diabetes and other endocrine disorders
- Cancer
- Obesity
- Physical injuries due to fall
- Alzheimer’s disease/dementia
- Depression, mental and emotional well being
- Substance abuse
- Respiratory diseases
- Other health problems that the elderly may have
List of the most common health concerns for the elderly and senior
These are the most common health concerns for elders and scenarios.
Find out what they are, how to prevent them and treat them.
Heart disease and stroke
Vascular disease in the heart and brain can occur as we age. A poor diet high in cholesterol and saturated fats, conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes and others can cause a narrowing or hardening of the arteries, and dysfunction in the vascular system.
The disruption in the blood flow to the heart or the brain can cause a heart attack or a stroke. This is more common in the elderly because they’ve had more time for the plague, which narrows the arteries, to build up. Therefore, they are more susceptible to other diseases that cause problems with blood flow to these vital organs.
Prevalence
Forty million Americans over the age of 60 have heart disease or stroke. That accounts for almost 75 percent of the overall prevalence for cardiovascular events (including CHD, or coronary heart disease, PAD or peripheral arterial disease, CHF or congestive heart failure, valvular diseases of the heart, high blood pressure and stroke).
Prevention
Prevention against cardiovascular disease and stroke can start long before a person reaches their senior years. These can prevent heart disease:
- Eating a heart healthy diet
- Getting regular aerobic exercise
- Managing other conditions, such as high blood pressure and diabetes,
Knowing your cholesterol numbers and working those numbers in a good range can help you to avoid problems with your vascular system that lead to heart disease and stroke. Watching your amounts of saturated fats, avoiding Trans fats, and taking cholesterol medication if needed may also help to prevent heart disease.1
Treatment
Treatments for cardiovascular disease are wide and varied. They include medications, procedures to open and unclog arteries and open-heart procedures. Treatment for early stroke signs includes emergency TPA (Tissue Plasminogen Activator), medications, rehabilitation therapies such as physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech therapy.
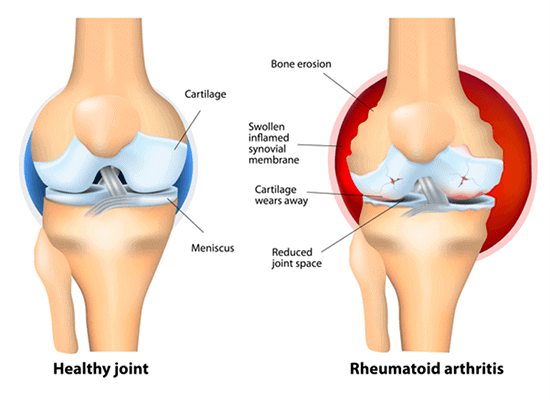
Arthritis
Osteoarthritis or inflamed joints with bone loss, and arthritis due to rheumatoid autoimmune arthritis affect the elderly more often than the rest of the population. Joints endure wear and tear from years of use, and joint replacements are common in this age group.
Prevalence
Arthritis, in fact, is the most common problem that seniors seem to have. Close to 50 percent of the elderly report osteoarthritis as the most common type. Other reported types of arthritis are reported are gout and rheumatoid arthritis, along with fibromyalgia. 2
Prevention
To prevent the onset of arthritis, stay active keeping your joints mobile. Watch your weight, and keep you Body Mass Index in a normal range for your height. To prevent gouts, there is a specific diet that is low in alcohols, sugars and purines. To prevent rheumatoid arthritis, stop smoking.
Your doctor will give you a list of foods to avoid if you are diagnosed with gout. Related to rheumatoid arthritis, it can be hereditary. Avoiding to smoke seems to delay the onset of symptoms.
Treatment
Treatments include NSAIDS (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as Motrin. There are a wide variety of arthritis pain medications. For gout, there is a special medication that the doctor will give you, along with a list of high uric acid foods to avoid.
Later treatments, when joints are at the end stage level of osteoarthritis, may include joint replacements or other procedures to open up the joint space.
Diabetes and other endocrine disorders
Metabolic disorders and diabetes, menopause and problems with thyroid function are all more common in the elderly population.
Hormones levels change as we age. Insulin production can decrease, as beta cells give out after years of use. The metabolism of fat and cholesterol in the diet changes, leading to overweight, and difficulty with losing weight gained.
Vitamin D and Calcium levels, as well as other electrolyte and vitamin and mineral levels can be disrupted in the elderly. Hormonal changes lead to problems with erectile dysfunction and vaginal dryness.
Prevalence
Over five million elderly people in the US have diabetes. That’s a prevalence of over 15 percent. 3
Prevention
Prevention of diabetes includes losing just five to seven percent of overall body weight if you are overweight, staying physically active and maintaining a healthy diet. Thyroid and other hormonal issues may not be preventable, but rather a normal part of the aging process.
Treatment
While there is no permanent reversal of diabetes once you have it, type 2 diabetes can be managed with diet and exercise. Treatments can also include oral medications, injectable medications, or insulins through injections, an insulin pump, or most recently, inhaled insulin.
Treatments for thyroid disorders include medications and surgeries. Erectile dysfunction can be treated with medications, and various other devices or surgical implants. Vaginal dryness can be treated with hormone therapy or over the counter lubricants.
Cancer
Cancer can occur just about anywhere in the body. It can spread to other parts of the body. It may be easy to treat, or may not even respond to treatment.
Prevalence
If you’re an elderly, you have 10 times more chance of developing cancer, and you have 16 times more chances of dying from cancer. This includes cancers of all types, from prostate, to lung, to breast, to colon, to pancreatic, and more. 4
Prevention
Prevention of cancer includes following a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight while getting regular exercise and avoidance of smoking and irritants, including chemicals from the environment. Today, it’s not so easy to avoid everything that can cause cancer. Here in North Carolina, we have 24 chemicals in our water due to the Chemours corporation polluting the Cape Fear River.
Getting necessary immunizations, such as Hepatitis B immunization can prevent liver cancer and vaccines for HBV, or Human Papilloma Virus prevent many types of cervical cancers. Practicing safe sex, and never sharing needles for diabetes or any other reason help to prevent blood borne infections.
Finally, see your health care provider regularly for cancer screenings and wellness checkups.
Treatment
Treatment of cancer can include removal of the tumor, chemotherapy, radiation or oral medications.
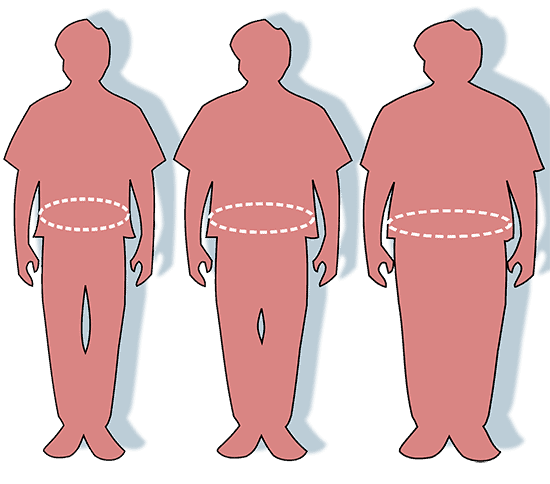
Obesity
Maintaining our optimal body weight as we age becomes more difficult. Our body redistributes fat to our abdominal areas, and it’s hard to lose it related to hormonal changes.
Obesity is a risk factor for high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, stroke, arthritis, sleep apnea, problems with cholesterol, and cancers.
Prevalence
Over one third senior age adults are obese. That is 13 million elderly individuals, which accounts for high medical costs considering obesity is a contributing factor to other chronic conditions. Tracking obesity will be important as the elderly population continues to grow.
Prevention
Working to lose even a small percentage of extra body weight can reduce your chances of getting many diseases. Prevention is key, and working towards overall wellness helps to prevent obesity and related health complications. A heart healthy diet and regular exercise is recommended. Working to move enough to work off the calories and energy from food we take in becomes important. 6
Treatment
Conservative treatment for obesity includes both a calorie controlled diet and an exercise plan. It may include support, or even counselling. There are medications for weight loss when such methods fail. Lap band and bariatric surgery are last resorts, but offer promise for the morbidly obese, and has been known to reverse diabetes in some cases.
I also suggest reading the following:
Physical injuries due to fall
Losing your balance is easy when you are a senior adult. Loss of muscle mass, coordination, arthritis and osteoporosis can lead to falls and fractures in the elderly.
Many evidenced-based programs in senior and community centers focus on fall prevention. There are programs such as Matter of Balance, Tai Chi and yoga designed to improve muscle coordination, fitness, strength and balance in senior adults.
A physical therapist may do a falls assessment in the home to remove scatter rugs, clutter, electrical cords and other objects that could cause a fall. In the bathroom, hand rails and wall mount bars may help, while walk in tubs provide help for those who can’t get into the tub.
Prevalence
About one third of elderly persons will experience a fall, with varying degrees of injury being sustained.
Prevention
Many evidenced-based programs in senior and community centers focus on fall prevention. There are programs such as Matter of Balance, Tai Chi and yoga designed to improve muscle coordination, fitness, strength and balance in senior adults.
A physical therapist may do a falls assessment in the home to remove scatter rugs, clutter, electrical cords and other objects that could cause a fall. In the bathroom, hand rails and wall mount bars may help, while walk in tubs provide help for those who can’t get into the tub.
Treatment
Once a fall has been experienced, treatments are given depending on the amount of injury sustained. They may need physical therapy, surgery to repair a fracture or hospitalization. Often, when the hip is broken, the elderly will require a hip replacement.
Severe injuries can lead to an elderly person’s decline in health, as further immobility leads to more issues. Falls remain a serious threat to the health of the elderly population, and prevention as opposed to treatment after the fact is preferable.
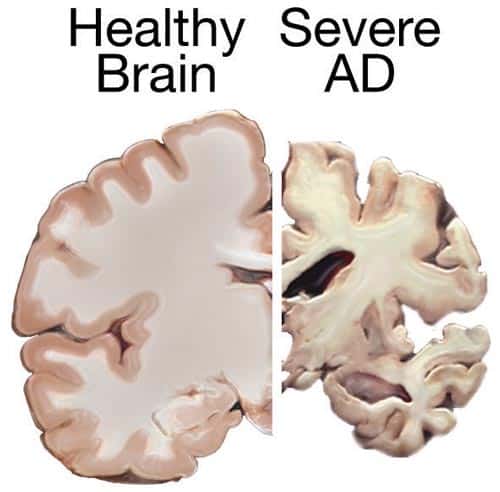
Alzheimer’s disease/dementia
Dementia means that your brain deteriorates, and cognition, behavior and ability to do activities of daily living are impaired. By far, older adults are more affected by dementia than the rest of the population. The most common form, known as Alzheimer’s Disease, is debilitating to patients and families, and comes with a high emotional and financial cost.
Prevention
Controlling diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure and depression symptoms, and avoiding smoking can help prevent dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
Prevalence
By far, seniors are more affected by dementia than the rest of the population. That doesn’t mean that it’s normal to lose your memory and thinking ability as you age. Over 47 million people have some form of dementia, and numbers are set to sky rocket three-fold by 2050. One third of those, which is about 15 million, are senior adults.
Treatment
If dementia or Alzheimer’s is diagnosed, there are then several medications that may help. There is currently no cure. Research into the effects of some diabetes drugs on dementia and Alzheimer patients are being done, with a potential promise for inhaled insulin.
Advanced care may include memory care, or “lock down” care. As Alzheimer’s patients approach end stage, they revert to infantile behavior and wandering which can be a safety issue for seniors and put great stress on family members who are provide care of such patients.
Depression, mental and emotional well being
Depression is an increasing problem as we age.
Prevention
Having good sleeping habits and avoiding isolation as much as possible by having a good support system around you can help to ward off symptoms of depression. Getting some exercise and eating properly also helps to prevent depression.
Prevalence
About 15 percent of the elderly are either depressed or have some mental disease. Almost seven percent of these elderly have depression.
Sometimes, depression can lead to suicide in the elderly. White elderly males have a high suicide rate when compared to other groups. Control of other chronic illnesses can be helpful. Programs that address wellness for the elderly can help people to cope.
Treatment
Treatment can include therapy and medications, finding a way for the elderly person to get out in the community and providing a social structure for support, such as senior centers.
Meals on wheels and other programs that help to provide nutrition and social support are also necessary treatments for depression in the elderly. Support groups offer help for caregivers, which is also important.
Substance abuse
You might not think drug and alcohol abuse is a problem in the senior population, but this could be far from the truth. The elderly seeking pain reliefs to manage chronic diseases have become addicted to opioids as well as other addictive substances such as sleeping pills and anti-anxiety medications. 1
Prevention
Prevention of drug abuse in seniors includes provider and family awareness so that issues are not missed, and careful prescribing of medications.
Prevalence
Two and a half million seniors have drug or alcohol addiction problems. The number is expected to reach five million by 2050.
Treatment
Treatments for addiction may vary based on the substance abused. Inpatient treatment is required in the most severe cases, where withdrawal may pose a safety risk to seniors.
Respiratory diseases
Respiratory diseases in seniors include COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, such as emphysema, asthma and bronchitis.
Prevention
Prevention involves avoidance of smoke from tobacco and smoking, avoidance of chemicals and respiratory irritants and getting regular exercise to keep pulmonary functioning to capacity.
Prevalence
Lung disease prevalence is greater in the elderly population. Ten percent of the elderly are diagnosed with COPD, and is the fifth leading cause of death in the elderly.
Treatment
Treatments can include oxygen, bronchial opening medications, antibiotics for infections, and oxygen therapy. Pulmonary rehabilitation may be ordered.
Further reading:
Other health problems that the elderly may have
The elderly population may also have problems with the following:
- Influenza, pneumonia and shingles – largely prevented with vaccinations and careful handwashing(important)
- Malnutrition due to isolation or lack of access to food – prevented by providing social support and meal delivery services
- Vision, hearing and sensory problems – prevented by managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, and remedied with glasses or hearing aids
- Oral health problems – prevented by good oral health in earlier years, management of chronic conditions and prompt treatment to dental issues
- Changes in bowel or bladder – healthy diet and managing weight by exercising may prevent issues, or treating with appropriate medications or surgeries 7
- The elderly on the lower end of the socioeconomic scale are affected by these things most often
TheDiabetesCouncil Article | Reviewed by Dr. Sergii Vasyliuk MD on May 23, 2020
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2797320/
- https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/data_statistics/arthritis-related-stats.htm
- http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/29/11/2415.shor
- https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/senior-health/common-issues/top-ten.aspx
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1500929/
- https://vitalrecord.tamhsc.edu/10-common-elderly-health-issues/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1500929/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3775793/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4578976/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4779902/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5408160/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3052294/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3709085/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3260944/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3221135/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4146436/