We know that the beta cells, in the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas produce, store, and secrete insulin. In addition to insulin, these multi-tasking super cells in our body also manage to produce two other peptide hormones called amylin and C-peptide. In Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes, the busy beta cells are deficient or absent.
Contents
What is Amylin?
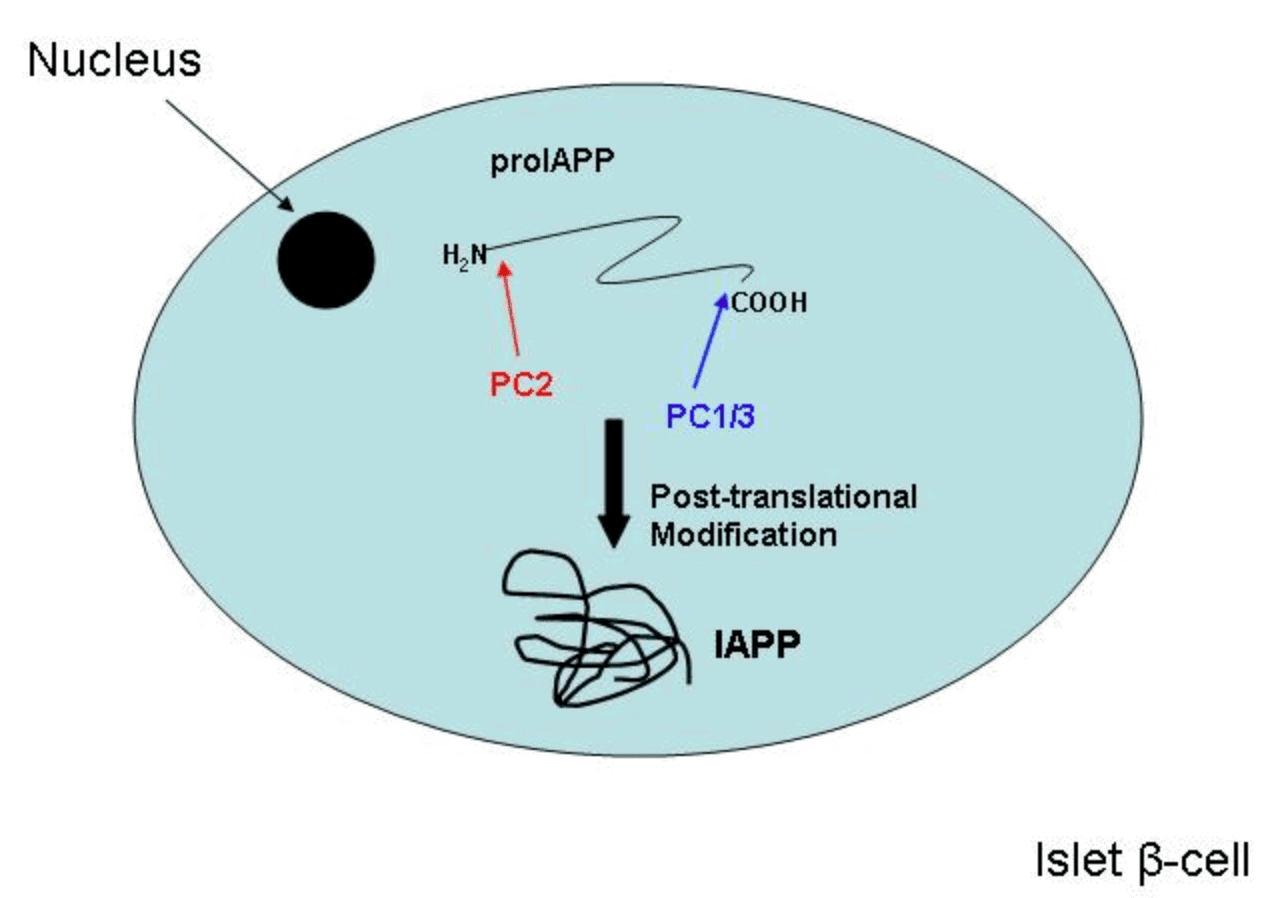
Amylin is not insulin. It is another peptide hormone produced by the beta cells in the pancreas. It acts as a gate keeper. It keeps sugar from entering the blood stream by halting glucagon secretion. It also slows gastric emptying, and curbs appetite.
While most people with diabetes may know about the beta cells, and their role in producing insulin, they may not be aware of insulin’s BFF, amylin. Amylin works alongside insulin to bring down blood sugars, curb appetite, and stop glucagon. Glucagon is basically more sugar that the liver releases.
When you have Type 1 Diabetes, your beta cells have all been attacked by your immune system, and you don’t make any amylin. You can benefit from injections of synthetic amylin. When you have Type 2 Diabetes, you may also benefit from synthetic amylin, since your body has a deficiency of amylin.
What is the role, or purpose of amylin in your body?
The purpose of amylin in blood sugar regulation is to prevent high blood sugar. This could be caused by food, stress, illness, or any other reasons for which the blood sugar may increase.
Amylin is important because it is secreted in equal amounts as insulin. Insulin is probably the most important hormone involved in regulating blood sugar, but it’s certainly not the only one.
As it turns out, without all the other parts, our endocrine team is not complete. All of the hormones involved in blood sugar metabolism are important, and they all work together like a team. Insulin, amylin, C-peptide, and glucagon, all work on your meals to bring down your blood sugar.
Insulin and amylin are of equal amounts when secreted. Though insulin is more popular, it can’t do its job without amylin. They play off each other, and they need each other.
Althea’s story
Althea came to me for help to better manage her Type 2 Diabetes. At 5 feet 4 inches and 260 pounds, she was morbidly obese. A quick look through her blood sugar log showed high post-meal blood sugars. Her doctor recommended her to take Symlin, a hormone he said she didn’t have much of.
It would help to regulate her blood sugars. She did not mind taking Symlin shots in addition to her insulin shots pre-meal, if it would help her to better control her blood sugars.
Althea started Symlin, and she did fine with the extra shots. She lost about 8 pounds, and her post-meal blood sugars were much better at her three-month follow-up. Overall, after starting Symlin, Althea had more energy to get out and do the things that she needed to do to get the extra weight off. Fast forward to one year later, Althea was down to 228 pounds. She is doing it slowly, but she is happy with the progress. She has needed less Symlin since then.
Althea’s doctor believes that she may have woken beta cells up from a long sleep, and they are now able to produce more insulin and amylin. Her A1C has gone down, and even after being taken off Symlin, Althea had post-meal blood sugars in the pre-diabetes range.
Is Symlin right for you? Let’s see why amylin is so important for people with diabetes.
Importance of Amylin for people with diabetes
Many people with diabetes are deficient in the hormone, due to the damage caused to the beta cells that manufacture it. It plays an important role in bringing down your post-meal blood sugars. Learning about amylin and how it might help one is beneficial for those with diabetes.
Once you have gathered enough knowledge about amylin, you can then decide if taking synthetic amylin is right for you. You can also decide if you want to try to wake your beta cells up, and get them to produce some amylin by themselves again.
Apart from insulin, lack of or deficiency in amylin is one of the reasons why blood sugars rise post-meal. We can choose to regulate our carbohydrates better, try to shake the beta cells awake with improved self-management, or alternatively take an injection of pre-meal of synthetic amylin to help with our post-meal blood sugar spikes.
I recommend reading the following articles:
How does Amylin work?
The mechanism of action by which amylin does this is by:
- Slowing the movement of food through the gastrointestinal system
- Blocking glucagon release from the liver
- Suppression of appetite
When amylin slows the emptying of our digestive tract (which basically slows down digestion), this prevents blood sugar from entering the blood steam at a rapid pace. Instead, blood sugar enters the blood stream at a slow, steady pace, preventing spikes in blood sugar, especially post-meal.
People taking amylin hormone don’t need as much pre-meal insulin, since they don’t have the extreme spikes in blood sugar.
Another reason amylin is important is that it is able to block glucagon release from the liver, which is a big deal in people with diabetes. If glucagon is allowed to be released every time your liver thinks you are starving, then you will have higher blood sugars.
Therefore, amylin is important in keeping blood sugar levels at a normal level, and steady rate. In the absence of amylin, when the beta cells in the pancreas are damaged, and they no longer produce enough or any amylin, blood sugars rise.
Where to find amylin?
Here is more information on how to get amylin.
The natural form is amylin
If your beta cells are worn out, as often happens in Type 2 Diabetes, you can wake them up by having better blood sugar control. All of the things that help Type 2 Diabetes to go into remission, or to manage it well, will work to help wake up your beta cells if they are not too far gone. This is how you crank up your own beta cells to begin manufacturing their own natural hormone amylin.
The synthetic form is Pramlintide (sold under the brand name, Symlin)
With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes, you can get the amylin that you lack for blood sugar control from injections of “Symlin,” or generic, Pramlintide, synthetic forms of amyline. This can help curb your post-meal blood sugar spikes while you work to wake up your beta cells if you have Type 2 Diabetes, or give you the amylin you need for Type 1.
If a person with diabetes is taking Symlin along with meal-time insulin, it is likely that their pre-meal dose of insulin will decrease. This is because Symlin will slow the digestion, and help to hold blood sugars steady. If you are taking Symlin and pre-meal insulin, expect your doctor to drop your dosage by about 10-20%.
In research, Symlin lowered A1C, fasting blood sugar, cholesterol levels (total and triglycerides), and kept people with diabetes in their target range post-meal. Also, as Symlin reduces spikes in blood sugar after a meal, it serves to help with the prevention of long-term complications associated with diabetes.
What is Symlin (Pramlintide)?
Symlin, or generic, Pramlintide, is the injection form of the hormone amylin. It is synthetic, or man-made. It performs the role of amylin, and helps both people with Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes who have to take insulin prevent post-meal blood sugar spikes.
If you have Type 1 Diabetes, and your beta cells have all been attacked by your immune system, and your body lacks amylin, you can benefit from injections of synthetic amylin. It is only for those with Type 2 Diabetes who take insulin though. If all you take is oral medications or GLP-1 injections for your Type 2 Diabetes, Symlin is not for you.
How and when should I take Symlin (Pramlintide)?
Symlin should be taken as a bolus dose along with insulin. You want to bolus it in an injection prior to meals. It’s very important to perform the bolus 5-10 minutes prior to meals. It takes quite a bit of effort at first to get Symlin working like your natural Amylin. Once it has kicked in, there can be significant benefits for the person with diabetes taking insulin.
What works and what doesn’t when adjusting Symlin dose?
Let’s discuss some tips to start Symlin off on the right foot. It seems a little cumbersome, but once the steps to the correct dosage for your individual needs are reached, you will not have to do much. Also, it’s important to note that all of this should be done under supervision by your physician or provider only.
Tips for starting Symlin
- Start Symlin dose with about 25% of usual insulin dose as a safe place to begin (with doctor’s supervision)
- Fine tune Symlin dose before deciding insulin dose
- Start with the lowest dose of Symlin – 15 mcg
- Increase dose by 15 mcg in increments
- Titrate dosage up until desired effect (blood glucose remains stable in target for several hours after meals)
- Start out taking Symlin at only one meal (breakfast is a good choice)
- After determining the dose for one meal, start injecting the same amount before your other meals
- The dose is the same at all meals. If adjustments are made, they must be for all meals
- Take Symlin 5-10 minutes before a meal
- Take Insulin 5-10 minutes after finishing the meal
- For hypoglycemia post-meal, with a rise a few hours later, switch to regular insulin if you take rapid insulin
- For insulin pump users, deliver bolus dose over 1-2 hours
- Check blood sugar an hour after eating during Symlin adjustment period
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) may be used
- Tolerance may be developed after several months or years to Symlin, and dose may need increasing
Taking your Symlin dose 5-10 minutes before eating, and then taking your insulin dose 5-10 minutes after your meal helps to get Symlin working right on time. You don’t want the medication to get into your system too fast, and cause a low blood sugar. For low blood sugar with rebound high blood sugar later on several hours post-meal, if you are taking rapid acting insulin, switch to regular insulin.
The reason for this is that rapid insulin goes to work in about 15 to 30 minutes, whereas regular insulin will take 30-45 minutes to start working. This will delay the onset of low blood sugar, and help the Symlin to work on the post-meal blood sugar to bring it down into target.
It’s important to specify that the insert for Symlin says that insulin dose should be 50% of previous dose prior to starting Symlin. Most people with diabetes who take Symlin will level off with about 10 to 20% insulin reduction. To be practical and reasonable, 25% has been shown to be a safe starting dose in most cases.
As uncomfortable as this may sound, if the Symlin dose is correct, you will either have a sour feeling in your stomach, and feel full 15-30 minutes after you inject Symlin; or you will have stable blood sugars for the hours following your meal. If you don’t get the sour feeling, or the stable blood sugars, your provider will need to increase your Symlin dose.
You can tell if your blood sugars are stable for several hours following meals by checking them with your glucometer, or you could rely on a CGM (Continuous Glucose Monitor), if you have one.
What is the recommended dosage of Symlin (Pramlintide)?
Symlin dosage is titrated up in 15 mcg increments and the dose is individualized based on patient blood sugar stabilization following meals.
How effective is Symlin (Pramlintide)?
Symlin is effective in mimicking the effects of the peptide hormone amylin in the human body. When there is no amylin to partner with insulin in keeping blood sugars down following meals, adding synthetic amylin to your diabetes regimen can help to get control on post-meal blood sugars.
Symlin can also lower A1C and cholesterol, and help you lose some weight. The drug may also help in avoiding long-term complications.
Do I need a prescription to be able to buy Symlin (Pramlintide)?
Your provider will need to write a prescription for this medication. In some cases, insurance companies may require special authorization.
How is Symlin delivered?
Symlin comes in an injection pen, similar to many insulins. Vials of Symlin have been discontinued. This doesn’t allow for much variability in the dosage of Symlin.
There are 2 sizes of Symlin pens. One is the starter dose, and one is a higher dose.
- Starter dose pen (delivers 15, 30, 45, or 60 mcg)
- Higher dose pen (delivers 60 or 120 mcg)
A small needle (5 or 6 mm) is used to inject Symlin subcutaneously, or just below the skin. Not much research has been done to see if Symlin is safe if delivered through an insulin pump. However, it seems that some people with Type 1 Diabetes do bolus dose with Symlin safely.
The tubing and cannula can get clogged with the medication, so a small basal dose of Symlin has been administered to counteract this problem. Talk with your healthcare provider, or endocrinologist before trying to infuse Symlin through an insulin pump.
What are the side effects of Symlin?
The most common side effect of synthetic amylin is nausea. About half of people with diabetes who have taken Symlin have some level of upset stomach. The peak of the medication is fifteen to thirty minutes after injection, therefore the “sour stomach” feeling usually occurs around that time.
The good news about the upset stomach with Symlin is that it does tend to subside after several weeks of drug therapy. The stomach issues are usually only a few minutes in duration, as they pass quickly.
Other side effects of Symlin include:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Vomiting
- Anorexia, or loss of appetite
- Stomach pain or cramps
- Tiredness
- Rhinitis, or runny nose
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Joint pain
- Headache
- Redness, swelling, or itching at injection site
Will Symlin interact with negatively with other medications that I take?
Some medications taken with Symlin can mask low blood sugars. They are:
- Albuterol
- Clonidine
- Cholesterol medications
- ACE inhibitors
Other medications taken with Symlin can cause a low blood sugar. They are:
- Probenecid
- NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Aspirin
- Sulfa
- MAOI’s for depression
- Beta blocker medications
High blood sugar can occur while taking Symlin if it is taken with the following medications:
- Idoniazid
- Diuretics (Lasix)
- Steroids
- Phenothiazines
- Thyroid medications
- Birth control pills
- Hormones
- Medications for seizures
- Diet pills
- Asthma medications
- Cold and allergy medications
Other medications may interact with Symlin. They are:
- Miglitol
- Belladonna
- Acarbose
- Atropine
- Dimenhydrinate
- Benztropine
- Scopolamine
- mepenzolate,
- methscopolamine
- bronchodilators
- glycopyrrolate
- urinary and bladder medications
- medications for IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
Additional risks for hypoglycemia unawareness
If your autonomic nervous system is out of control and you have low blood sugars before you realize it, then you probably have “hypoglycemia unawareness.” This can give you some additional risks when taking Symlin.
Remember that with Symlin, your food digests more slowly than it would if you didn’t have Symlin in your system. Since pre-meal insulin could also cause low blood sugar, this is the reason to delay taking insulin until 5-10 minutes after you finish eating.
It’s not advisable to take Symlin if your blood sugar is already low before the meal. You would want to hold the Symlin dose in this case.
Exercising after a meal can also precipitate a low blood sugar when you are taking Symlin. This is particularly true if the foods you ate are high in fiber, and tend to digest slowly.
It’s tough to treat low blood sugar when you are taking Symlin, because it is specifically working on bringing those post-meal blood sugars down. It blocks the glucagon from being released from the liver, and slows down digestion in your gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, treating low blood sugar with 15 grams of quick acting carbohydrates by conventional method may not work.
You may have to use glucose tablets or gel under your tongue to seep into the blood stream, and hold it there over time. You may even require a glucagon injection. Speak with your healthcare provider about whether or not you need a prescription for a glucagon pen if you are taking Symlin. 1
Things to consider
There are some things to consider when taking Symlin besides the difficulty with dosage adjustment in the beginning. Some are:
- Its an injection, not a pill
- You can’t mix it with insulin
- You must take a separate injection pre-meal
- It’s expensive
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does Symlin cost?
Symlin is a very expensive medication for diabetes. A box of the pens is just as expensive as a box of insulin pens.
Though most health insurance plans may cover Symlin for Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes who are also taking insulin, your doctor or healthcare provider will most always have to jump through some insurance company hoops to get your Symlin covered. It generally requires a prior authorization process, which means paperwork for your doctor, and waiting to see if your medication is covered for you.
There will likely be a high co-payment for Symlin. If you do not have insurance, or you are under-insured, the company that makes Symlin has a patient prescription assistance program available. The link for the amylin website is here: Amylin.com
However, at publication date of this article, the Amylin website has changed domain.
How can Amylin help lose weight?
When you have diabetes, and your blood sugars are high, you tend to be hungry all the time. All of the blood sugar is just sitting in the blood stream. It is not getting to the inside of your body’s cells. Since it is not “feeding” your body cells, the sensation is that you are still hungry. The body cells give this signal to the brain, where they can sense the blood sugar just out of reach, but they can’t get to it for nourishment. This process is part of the hungry feelings that continue.
The other reason for this is the lack of amylin. Since you don’t have the appetite suppression that amylin produces in your system, you feel hungry. For these two reasons, it is very difficult for people with diabetes to lose weight.
Symlin, while providing your body with amylin-like appetite suppression that it needs, and by keeping down post-meal blood sugars, it can also help you to lose weight. Sometime between 15 and 30 minutes after taking a Symlin injection, you feel the “sour stomach,” or you just feel full. This leads to eating less. As your portions get smaller, so does your waist.
After a meal, Symlin will keep you feeling full. However, weight loss with Symlin is moderate, with only about six pounds lost over a six-month period. Still, combined with diet and exercise, it could be a useful medication to help some patients lose weight. 2
How do I know that Symlin is working?
You will know that Symlin is working when you feel the “sour stomach” or full feeling that comes on about 15 to 30 minutes following the injections, and if your post-meal blood sugars remain stable in your target range for at least 2-3 hours following the meal.
What is the best way to take Symlin?
You will need to follow the process for titrating Symlin and determining the dose with your doctor’s supervision. Once you have figured out what your dose of Symlin should be, and how much of a percentage you should lower your insulin dose to go along with it, things will level off. There is a process, and your healthcare team is there to help you figure it all out.
It may take you a while to get to a stable blood sugar post-meal with Symlin. The process usually takes about three weeks to accomplish after which your regimen will then get easier.
Do I need to watch my diet and eating habits while on Amylin?
Yes, you have diabetes, so you should be eating an appropriate amount of carbohydrates (which means counting them!). You should eat heart healthy, increasing good fats in your diet, decreasing bad fats, and watching your salt intake. Amylin is one hormone that helps in the regulation of blood sugars. Taking Symlin is not going to mean that you can leave your other self-management behaviors by the wayside.
What is the difference between Amylin and Amylin extended release?
Symlin only comes in one formulation, and it is not available in an regular release versus an extended release formula. Symlin releases over several hours, following your meal.
Are there other alternates for Amylin?
No, there are no alternative medications. Symlin (Pranlintide) is the only medication that mimics the hormone amylin produce in the human body.
Can I take Symlin while I am pregnant?
Before you start taking Symlin, let your doctor know if you are pregnant, or if you are planning to become pregnant in the future. Symlin is a pregnancy category C drug, which means that it’s used only if benefits outweigh risks in pregnancy. It hasn’t been studied in pregnant women. 3
Can I take Symlin if I am breastfeeding?
Currently, we don’t know if Symlin passes into breast milk. Therefore, we don’t know if Symlin is safe for a nursing baby.
Tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding. It is not known if pramlintide passes into your milk and if it can harm your baby. You and your doctor will decide the best way to feed your baby if you are using pramlintide.
Does Symlin need to be taken at the same time everyday?
Symlin is to be taken at the same time every day, which is 5-10 minutes prior to eating a meal.
Can I take it at the same time as other medications?
Yes, you take Symlin about the same time that you take your pre-meal insulin. However, refer to the list of medications that interact with Symlin above. Also, make sure to check with your doctor or pharmacist about any interactions that may occur with other medications that you take.
Is Symlin (Pramlintide) approved for children?
No, Symlin is not approved for children. There have been a few studies that show it to be safe and effective when treating diabetes in the adolescent population. Doctors can choose to prescribe Symlin off-label to those under the age of 18.
How do I know it’s for me?
People who are having trouble getting their A1C down, especially after other medications and interventions have failed, may want to try synthetic amylin. People with Type 2 Diabetes who are extremely insulin resistant may benefit from dosages of this medication prior to meals.
If you think that synthetic amylin injections are right for you, have a conversation with your healthcare provider to see if you could be a candidate to try it.
How often is lactic acidosis reported with Symlin use?
In patients with kidney failure and in the elderly, Symlin has rarely caused a metabolic condition called lactic acidosis in patients taking Symlin, and the oral diabetes medication metformin. Lactic acidosis happens when lactate builds up in our body and causes our pH balance to go dangerously low. This is a condition of metabolic acidosis, and results from a problem with metabolism of lactic acid.
Further reading:
Amylin in research
Amylin in research has been found to play an important role in the management of blood sugar levels in the body. Amylin plays role in protecting the body from immune responses and inflammation. A normal level of Amylin is associated with a decreased risk of Type 1 Diabetes. Amylin may play a role in boosting the body’s autoimmune system and decreasing the risk of other autoimmune diseases, allergic responses, rejection of transplanted organs. 4
We hope that this article has shed some light into the complex world of amylin. Please leave your comments in the box below. We love to hear from our readers. We appreciate any feeedback that can help us better serve you in the future. Hopefully you find our Amylin overview useful and share with anyone who might need it.
TheDiabetesCouncil Article | Reviewed by Dr. Sergii Vasyliuk MD on May 18, 2020
References: