Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects your blood sugar levels. It’s a serious disease that can cause health problems if not appropriately managed. However, diabetes also has some unexpected side effects you may not be aware of.
Contents
- 1. Obstructive sleep apnoea
- 2. High blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- 3. Increased risk of kidney disease
- 4. Nerve damage
- 5. Gum disease
- 6. Skin infections
- Diabetes can be challenging to control and may have unexpected side effects
- How to better manage side effects of diabetes
- Knowing the side effects of diabetes
1. Obstructive sleep apnoea
You may have heard of obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) before. OSA is a condition where you briefly stop breathing during sleep, sometimes 30 or more times per hour. If you have OSA, your airway becomes blocked either by the tissues in your throat relaxing and collapsing into it or by an imbalance between your tongue and the floor of your mouth that makes it hard for air to flow through.
The symptoms include loud snoring (sometimes so loud that others can hear), waking up with a dry mouth, and feeling tired all day long. You might also wake up with headaches or feel like you’re getting enough sleep but still feel tired when you wake up every morning.
If left untreated, OSA can lead to heart disease and stroke, so it’s essential to learn about risk factors for developing this condition, like diabetes.
2. High blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
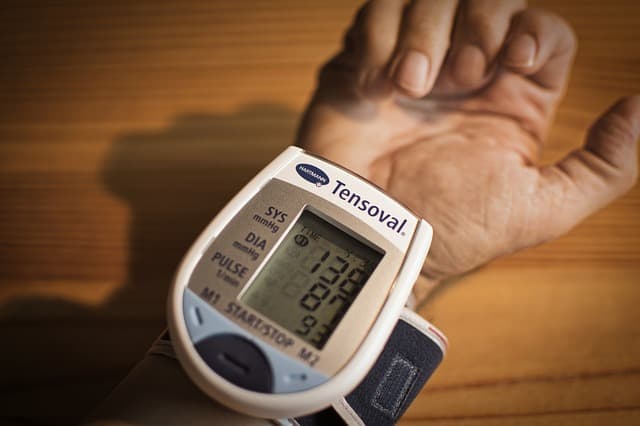
Diabetes can also lead to high blood pressure. High blood pressure—also known as hypertension—is when the force of blood against your artery walls is too high. The extra force may cause damage to the lining of your arteries and make them narrower, which increases the risk for heart disease and stroke. If you have diabetes, you're more likely to develop high blood pressure than someone who doesn't have diabetes.
Blood cholesterol levels also tend to be higher in people with diabetes than in those without it. Having high cholesterol puts you at greater risk for heart disease, which is one of many reasons why this condition must be closely monitored by your doctor if you have diabetes.
Another common issue that occurs when you have both conditions together is called "insulin resistance," which refers to how well cells respond to insulin (a hormone produced by the pancreas). Cells need insulin so they can take in glucose from foods we eat and use it as energy; however, if there's not enough insulin available or if cells become resistant to its actions (both possible side effects of having type 2), then your body may produce extra glucose instead of using what's already present inside them - leading directly back into where we started: increased haemoglobin A1c levels!
3. Increased risk of kidney disease
Kidney disease is another common complication of diabetes, and it can lead to kidney failure. In fact, kidney disease is one of the most common causes of death in people with diabetes.
Kidney disease occurs when your kidneys are damaged beyond their ability to filter waste products from your bloodstream. This may make you lose fluids, which can cause dehydration (a serious condition), or it may cause you to retain too much fluid. This can lead to swelling (edema) or an accumulation of salt and water in tissues that causes them to swell up (pitting edema).
It's essential for people with type 2 diabetes not only to manage their blood glucose but also to keep their blood pressure under control through exercise and diet changes like eating less sodium than normal while increasing fibre intake by eating more fruits and vegetables every day.
4. Nerve damage
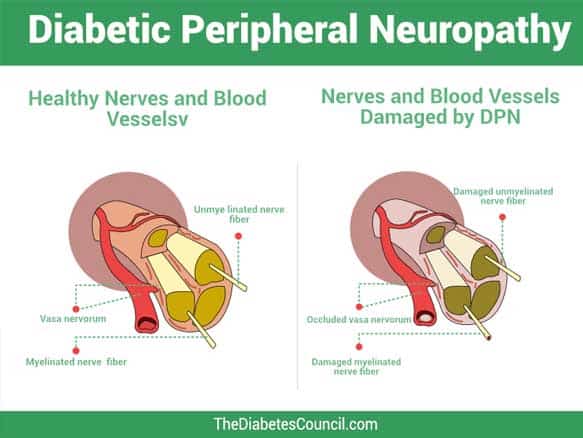
Nerve damage is one of the most common side effects of long-term diabetes. It occurs due to damage to blood vessels that supply blood to your nerves, which can make you feel numb or tingly in certain areas. Nerve damage might also cause weakness and loss of sensation in your feet, hands, and legs.
Diabetes can also cause nerve problems that affect your ability to move around safely and easily:
- Numbness or tingling in the feet (peripheral neuropathy)
- Weakness and loss of sensation in the feet (peripheral neuropathy)
- Painful burning sensation (neuropathic pain)
- Muscle cramps
Nerve pain is one example of neuropathic pain -- a type of chronic pain caused by damaged nerves in diabetic patients. Neuropathic pain affects about 30 per cent of people with diabetes but may be underreported because people don't realize they've got this serious complication; often, it's mistaken for other conditions such as fibromyalgia or arthritis.
5. Gum disease

If you have diabetes, you're at higher risk for gum disease. Diabetes can damage blood vessels in your mouth, which leads to bleeding. This can make it harder for your body to fight infection and keep bacteria from growing in your mouth.
Diabetes also causes dry mouth because of changes in the way your brain sends signals to your salivary glands (the structures that make spit). Food can get stuck in your teeth more easily without enough saliva and cause more plaque buildup.
Bad breath may be another symptom of diabetes — but don't worry: It's usually only temporary! If you've recently been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (or if you've had it a while), start doing these things right away:
- Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss once daily after brushing and rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash like Listerine Zero every night before bedtime — this will help kill germs that cause bad breath!
- Visit the dentist regularly for cleanings (the American Dental Association recommends every six months).
6. Skin infections
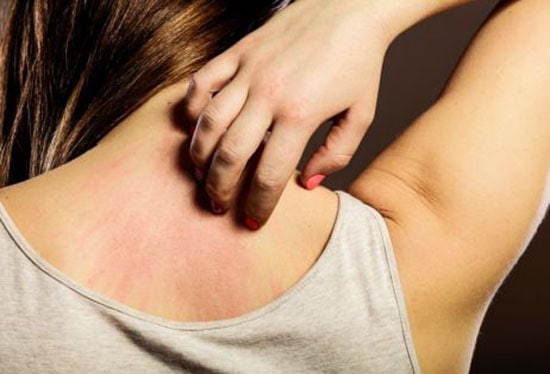
Skin infections are one of the most common side effects of diabetes. This can be caused by poor circulation and blood flow to the skin, making it difficult for wounds to heal. Diabetes also affects your immune system, making it more difficult for your body to fight off infections. In addition, some diabetic medications can cause you to get sick more often or at a faster pace than someone without diabetes would get sick.
When this happens, you might start noticing small red bumps that look like pimples on different parts of your body (e.g., legs).
These bumps may ooze pus when scratched or squeezed and usually don’t require any treatment except for letting them heal naturally – although if they are painful or uncomfortable, then try applying an antibiotic cream over them after cleaning off any pus from underneath with warm water and soap then drying with a towel afterwards before applying the cream once again in order ensure maximum effectiveness against these conditions!
Diabetes can be challenging to control and may have unexpected side effects

Diabetes is a lifelong disease that can be managed through diet, exercise, and medication. However, diabetes can also have unexpected side effects that you should be aware of. Let's take a look at some of the most common side effects of diabetes:
Nerve damage — Diabetic neuropathy occurs when high blood sugar damages nerves in your body. This can cause numbness or tingle in your hands or feet and pain that often wakes people up at night. Some more serious forms of diabetic neuropathy may lead to permanent nerve damage in your limbs and even amputation.
Kidney damage — Diabetes increases your chances for kidney disease because it narrows the arteries that supply blood to these organs by stiffening them with cholesterol deposits (atherosclerosis).
If not treated soon enough, this can result in kidney failure or even cause death due to infection or bleeding into an infected wound caused by poor blood flow through atherosclerotic arteries around the kidneys.
However, several treatments available today allow patients with kidney problems due to elevated glucose levels from having symptoms early enough, so they don't need dialysis later on after years worth of time has passed without proper treatment being received first!
How to better manage side effects of diabetes
To better manage any symptoms of diabetes, you'll want to incorporate healthy habits into your daily routine.
Eat a healthy diet

This can include lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains, but it's also vital that you limit your intake of foods high in sugar or fat.
Exercise regularly
Even if you're not able to exercise for long periods at a time, simply getting up from the couch once per hour will count as physical activity! Try walking around the block or taking a dance class.
If these seem too ambitious (or if you live somewhere where such options don't exist), consider doing simple exercises while watching television or listening to music—it may help lower blood pressure levels while giving both mind and body something productive to do!
Take medications as prescribed by your doctor

Be sure not only that you are taking this medication on schedule but also how much medicine they have suggested for each dose; these details should be included in any written instructions provided by medical professionals when starting treatment with insulin pumps, pills, or other types of medications used specifically for managing side effects associated with diabetes mellitus type 2 disease conditions.
Knowing the side effects of diabetes
So, now you know the different types of diabetes and some of the major causes. You may have been diagnosed with one or more of these conditions, which means that you’ll need to take certain steps to manage them effectively.
By staying informed about your symptoms and working closely with your doctor, there’s no reason why you can’t live a long and healthy life as a diabetic person!





